
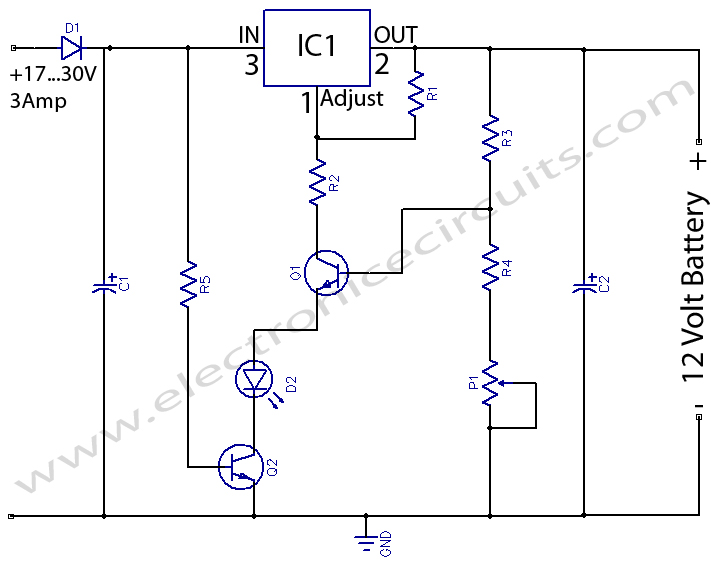
12 Volts Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit
Except for use as a normal Batter Charger, this circuit is perfect to ‘constant-charge’ a 12-Volt Lead-Acid Battery, like the one in your flight box, and keep it in optimum charged condition. This circuit is not recommended for GEL-TYPE batteries since it draws to much current.
| PARTS LIST | |
| R1 | 120Ω |
| R2 | 82Ω |
| R3 | 10KΩ |
| R4 | 33KΩ |
| R5 | 22KΩ |
| P1 | 2.2KΩ |
| C1 | 10µF 63V |
| C2 | 10µF 63V |
| D1 | IN5401 |
| D2 | LED |
| Q1 | BD140 |
| Q2 | BC547 |
| IC1 | LM350K OR LM350T |
The above circuit is a precision voltage source, and contains a temperature sensor with a negative temperature coëficient. Meaning, whenever the surrounding or battery temperature increases the voltage will automatically decrease. Temperature coëficient for this circuit is -8mV per °Celcius. A normal transistor (Q1) is used as a temperature sensor.
This Battery Charger is centered around the LM350 integrated, 3-amp, adjustable stabilizer IC. Output voltage can be adjusted with P1 between 13.5 and 14.5 volt. T2 was added to prevent battery discharge via R1 if no power present. P1 can adjust the output voltage between 13.5 and 14.5 volts. R4’s value can be adjusted to accommodate a bit larger or smaller window. D1 is a large power-diode, 100V PRV @ 3 amp. Bigger is best but I don’t recommend going smaller.

The LM350’s ‘adjust’ pin will try to keep the voltage drop between its pin and the output pin at a constant value of 1.25V. So there is a constant current flow through R1. Q1 act here as a temperature sensor with the help of components P1/R3/R4 who more or less control the base of Q1. Since the emitter/base connection of Q1, just like any other semiconductor, contains a temperature coëficient of -2mV/°C, the output voltage will also show a negative temperature coëficient. That one is only a factor of 4 larger, because of the variation of the emitter/basis of Q1 multiplied by the division factor of P1/R3/R4. Which results in approximately -8mV/°C. To prevent that sensor Q1 is warmed up by its own current draw, I recommend adding a cooling rib of sorts.
(If you wish to compensate for the battery-temperature itself, then Q1 should be mounted as close on the battery as possible)
The red led (D2) indicates the presence of input power.

Depending on what type of transistor you use for Q1, the pads on the circuit board may not fit exactly (in case of the BD140).
Caution: Adjust the voltage of capacitor C1 according to the input voltage. Example, if your input voltage will be 24 volt, your C1 should be able to carry at least 50V.
Please send your ideas, which are very important for our success…
hi………….
it is very simple circuit.i want to build it and i want to ask one thing what is the input and output of this circuit.second what is p1.
Sir why did u say that Q1 acts as a negative coefficient sensor,I am not convinced with that also the LED u said that act as indication of power, in my analysis correct me if I am wrong,as the battery is at its discharge condition Q1 is cutoff and only saturates when the battery reaches full charge accdg to the reference voltage given to the node of R3 and R4 which in turn swithes the LED indicating full charge……….thanks